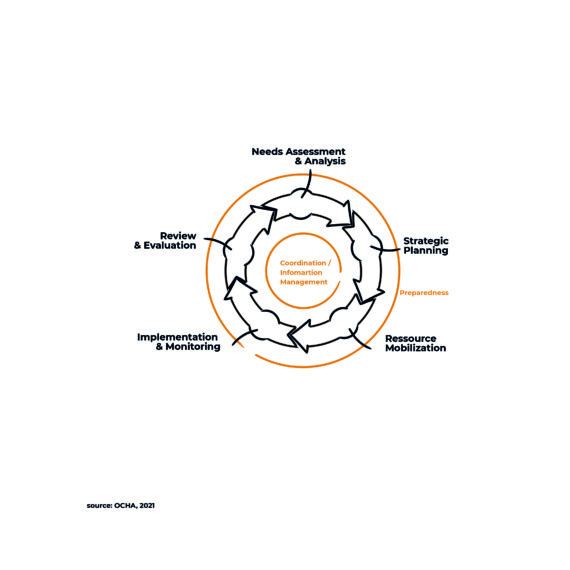
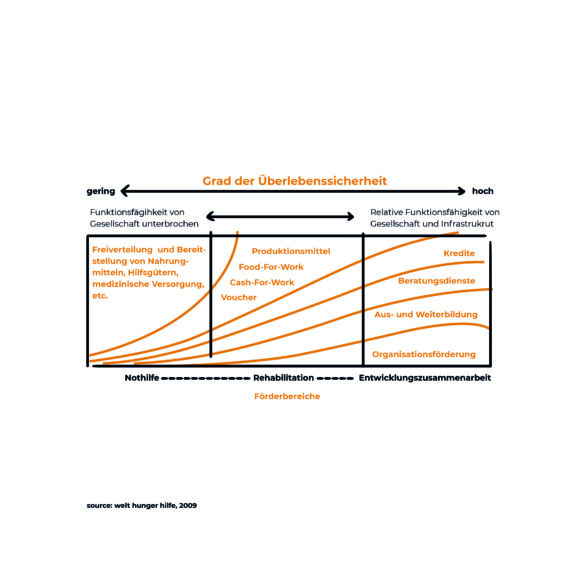
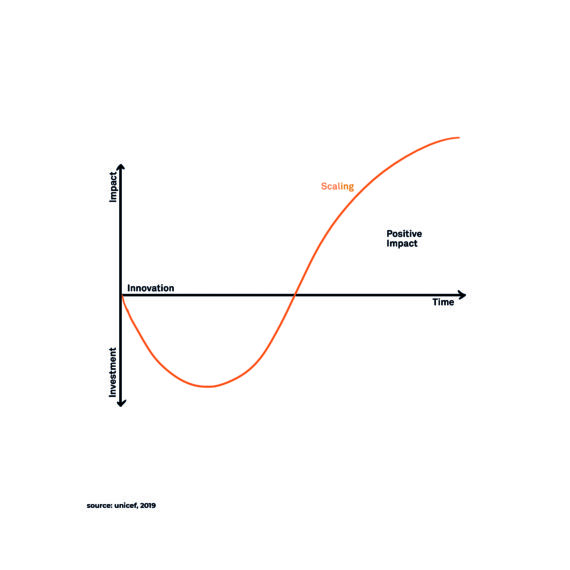
Humanitarian Innovation
Humanitarian innovation is currently being discussed and
first came in 2009, initiated by the UN
Working group on. The humanitarian sector worked
the last few decades using a top-down approach, i.e. help in the form of gifts.
As a result, social groups affected by crises and disasters have become dependent on organizations. So were
although it has an effect of alleviating suffering, it does
Crises not overcome in the long term. The previous
Approaches rarely worked efficiently with local circumstances and the needs of those affected. Aid organizations remained so to individuals
crises bound while global are numerous more appeared. Attempts were made to overburden this qualitatively determined, quantitative overburden with larger ones.
To deal with expenses. More funding was mobilized and the number of humanitarian projects in doubled over the past thirty years.
Under the topic of Humanitarian Innovation
are now new paradigms of work, such as help for
Self-help discussed and differentiated from this more qualitative
Hopes for projects that will sustainably overcome the crises,
meet the need and the person concerned empowers theirs
Solve problems yourself.
In order to make the sector more efficient, it is opening up
Humanitarian Innovation
Humanitarian innovation is currently being discussed and
first came in 2009, initiated by the UN
Working group on. The humanitarian sector worked
the last few decades using a top-down approach, i.e. help in the form of gifts.
As a result, social groups affected by crises and disasters have become dependent on organizations. So were
although it has an effect of alleviating suffering, it does
Crises not overcome in the long term. The previous
Approaches rarely worked efficiently with local circumstances and the needs of those affected. Aid organizations remained so to individuals
crises bound while global are numerous more appeared. Attempts were made to overburden this qualitatively determined, quantitative overburden with larger ones.
To deal with expenses. More funding was mobilized and the number of humanitarian projects in doubled over the past thirty years.
Under the topic of Humanitarian Innovation
are now new paradigms of work, such as help for
Self-help discussed and differentiated from this more qualitative
Hopes for projects that will sustainably overcome the crises,
meet the need and the person concerned empowers theirs
Solve problems yourself.
In order to make the sector more efficient, it is opening up
Humanitarian Innovation
Humanitarian innovation is currently being discussed and
first came in 2009, initiated by the UN
Working group on. The humanitarian sector worked
the last few decades using a top-down approach, i.e. help in the form of gifts.
As a result, social groups affected by crises and disasters have become dependent on organizations. So were
although it has an effect of alleviating suffering, it does
Crises not overcome in the long term. The previous
Approaches rarely worked efficiently with local circumstances and the needs of those affected. Aid organizations remained so to individuals
crises bound while global are numerous more appeared. Attempts were made to overburden this qualitatively determined, quantitative overburden with larger ones.
To deal with expenses. More funding was mobilized and the number of humanitarian projects in doubled over the past thirty years.
Under the topic of Humanitarian Innovation
are now new paradigms of work, such as help for
Self-help discussed and differentiated from this more qualitative
Hopes for projects that will sustainably overcome the crises,
meet the need and the person concerned empowers theirs
Solve problems yourself.
In order to make the sector more efficient, it is opening up
Humanitarian Innovation
Humanitarian innovation is currently being discussed and
first came in 2009, initiated by the UN
Working group on. The humanitarian sector worked
the last few decades using a top-down approach, i.e. help in the form of gifts.
As a result, social groups affected by crises and disasters have become dependent on organizations. So were
although it has an effect of alleviating suffering, it does
Crises not overcome in the long term. The previous
Approaches rarely worked efficiently with local circumstances and the needs of those affected. Aid organizations remained so to individuals
crises bound while global are numerous more appeared. Attempts were made to overburden this qualitatively determined, quantitative overburden with larger ones.
To deal with expenses. More funding was mobilized and the number of humanitarian projects in doubled over the past thirty years.
Under the topic of Humanitarian Innovation
are now new paradigms of work, such as help for
Self-help discussed and differentiated from this more qualitative
Hopes for projects that will sustainably overcome the crises,
meet the need and the person concerned empowers theirs
Solve problems yourself.
In order to make the sector more efficient, it is opening up
Empowerment
In order to make the sector more efficient, it is opening up
under this umbrella term of „Humanitarian Innovation“.
It’s about means of new partners, to whom now
the affected population also belongs to that.
To provide services and / or products,
what overcomes the crisis most sustainably and with the greatest possible efficiency. The expertise like products
and systems are to be optimized, lives in the work
from the designer: inside. Still, they have been so far
in the studies of humanitarian innovation
not integrated in this ecosystem. So it stays closed
Discuss which role designers can potentially play within the project and sector, and which role
This adds value to the humanitarian ecosystem and
can generate especially for those affected.
The factor of helping people to help themselves is currently considered a principle, which could relieve the sector.
Here, power relationships between organizations and those affected are discussed. Power must be a fluid potential and result of the empowerment process
be understood. This is the only way people can get into the
Process of the humanitarian project started and
be empowered. For this you have to support them multidimensionally. All five types of qualification:
Economic, psychological, educational, political and social skills must be taken as a unit
be understood.
Design expertise
These empowerment processes must now be compared with design processes and organizationally combined.
Power relations in the design process are shown. These indicate that a process that the
Users should be able to empower, initially a participatory one who understands power as fluid potential and
is committed to the best possible result. A goal-oriented design process is neither top down nor
bottom up. The situational knowledge of the users: inside and
the expertise of designers and organizations
must be symbiotic in a process on an equal footing
be united. This process takes place on site and
sees the use of the design as part of the design. To get the best possible results, you should
Designers: as many as possible in this process
Have interfaces in the ecosystem of the project
and directly into the mission cycle of the organizations
to be involved. Klaus Krippendorf lists that
The success of designers lies in their communicative ability. By means of this they can do it
To build consensus between the partners‘ expert knowledge,
to discuss the best possible practicable and the
To make the wishes and fears of those involved heard in the process. So they are just the ones
which are in the process of finding a new ecosystem,
become the mediators of innovation.
Humanitarian Design
Here, by means of an iterative design process, they enable new solutions to be found that overcome the previous status quo. This can be done on both
the restructuring of humanitarian innovation,
as well as applied to the projects themselves.
Designer: inside enable a general added value for the entire, as well as project-specific
Process of finding efficiency.
A holistic efficiency of the sector is also
not only through the participation of users and the
enabling and meeting the
Possible as required. It also requires standardized reproducibility, the outdated notions
overcome by neocolonialism. This fear of
Neocolonization keeps people from what
them to a life of dignity or a survival
need because you don’t see western culture
want to impose.
However, the effect of drafts in relation to form and context can be scientifically evaluated and if so
the needs of homo sapiens are thereby satisfied
a possible global application,
to which we as a society are morally obliged,
occur. This is exactly where the greatest added value lies
the involvement of designers. You can
to imagine contextually adequate solutions
and to give them reproducibility. Around
ensure that these can really meet local needs
for example, on the smallest possible intervention, such as
Burkhardt describes him, or the provocation of the
Adaptation, available from Bredies.
This creates standardized solutions that
not for every context with immense effort
have to be redeveloped and yet despite
Reproducibility in participation developed and
being checked. Designer: inside are exactly those who
Make the efficiency of the sector holistic. To do this too
must enable cooperation between
Organizations and designers: promoted and
further researched.